编者按:此篇文章为我室王润国博士在Macromolecules发表的文章。介绍了我室在生物弹性体方面的最新研究成果。
Design and Preparation of a Novel Cross-Linkable, High Molecular Weight, and Bio-Based Elastomer by Emulsion Polymerizationt
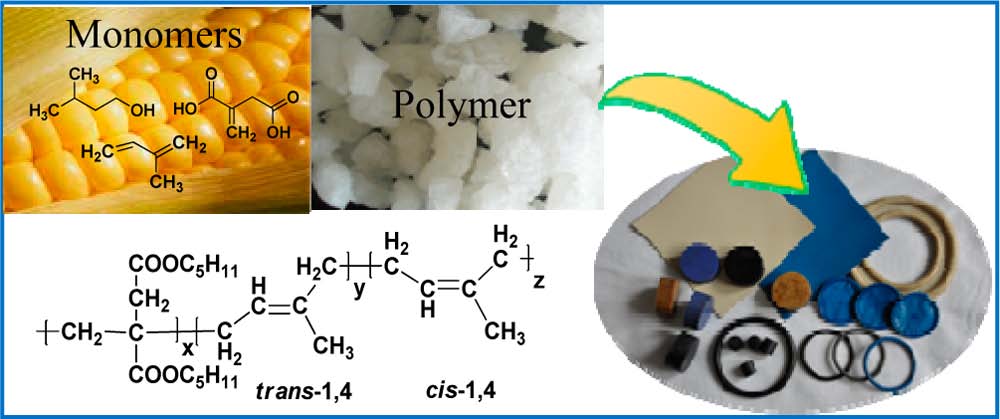
A novel cross-linkable, high molecular weight poly(diisoamyl itaconate-co-isoprene) (PDII) elastomer was prepared by emulsion polymerization based on itaconic acid, isoamyl alcohol, and isoprene. Both persulfate and redox initiators were used for the copolymerization of diisoamylitaconate and isoprene at different monomer ratios. Redoxinitiated PDII has much higher molecular weight but relatively lower yield than the persulfate-initiated one. PDII with a number-average molecular weight of 352 000 and a glass transition temperature of −39.5 °C was obtained when themass ratio of diisoamyl itaconate to isoprene was 80/20. Diisoamyl itaconate and isoprene reactivity ratios were determined by two conventional linear methods: the Fineman−Ross method and the Kelen−Tu?do?s method. Molecular dynamics simulation and FTIR were used to study the interaction between silica and PDII macromolecules, and the result showed that hydrogen bonds were formed between silica silanols and PDII macromolecules. Silica-reinforced PDII exhibited good mechanical performance, such as ultimate tensile strength above 11 MPa and elongation at break above 400%.